Air pollution is one of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time, affecting the health of millions of people and the integrity of ecosystems worldwide. It is defined as the presence of harmful substances in the atmosphere, which can be either natural or man-made. The sources of air pollution are diverse, ranging from industrial emissions and vehicle exhaust to household products and agricultural practices. As urbanization and industrialization continue to rise, the urgency to address air pollution has never been greater.
Objectives
The primary objectives of addressing air pollution include:
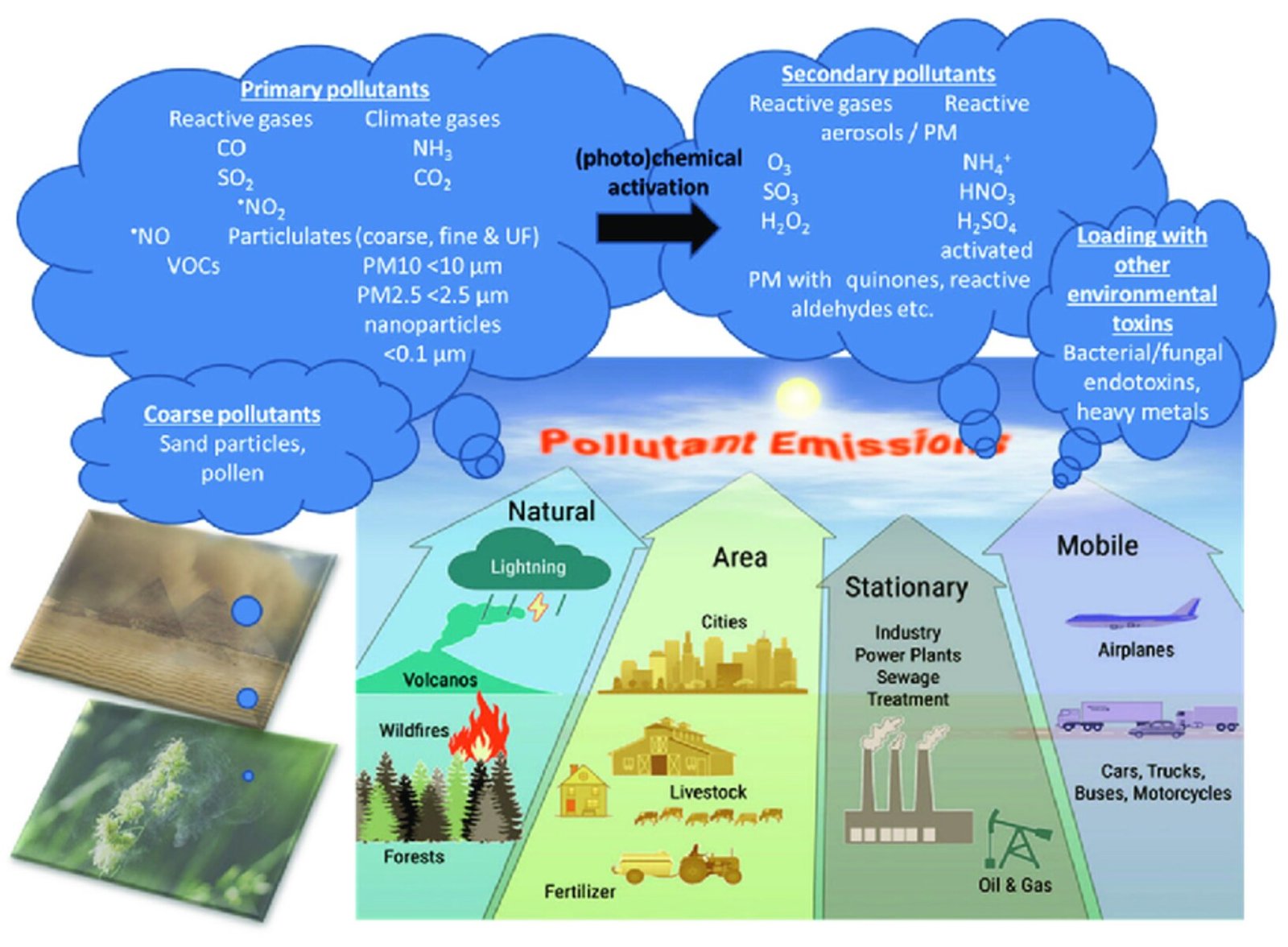
Types of Air Pollution
Air pollution can be categorized into two main types:
Table of Air Pollutants and Their Limits
|
Pollutant |
Source |
WHO Limit (µg/m³) |
|
PM2.5 |
Combustion, industrial |
10 |
|
PM10 |
Dust, pollen, smoke |
20 |
|
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) |
Vehicle emissions |
40 |
|
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) |
Fossil fuel combustion |
20 |
|
Carbon Monoxide (CO) |
Incomplete combustion |
10 |
|
Ozone (O3) |
Secondary pollutant |
180 |

Health Effects
Air pollution has severe health implications, affecting both short-term and long-term health outcomes. Key health effects include:
Environmental and Ecological Impacts
Air pollution not only affects human health but also has profound impacts on the environment and ecosystems. Key environmental and ecological impacts include:
How to Reduce Impacts
Reducing the impacts of air pollution requires concerted efforts at individual, community, and governmental levels. Strategies include:
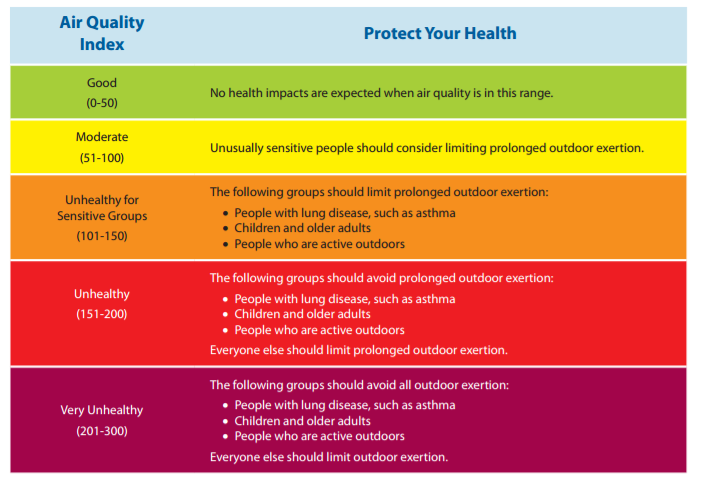
Monitoring Air Quality
Effective monitoring of air quality is essential for understanding pollution levels and protecting public health. Methods include:
Sustainable Steps to Combat Air Pollution
Sustainable practices play a vital role in reducing air pollution. Key steps include:

Comparative Air Pollution Status in Major Indian Cities
India faces significant air quality challenges, particularly in major cities. Cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Kolkata often report alarming levels of PM2.5 and NO2, frequently exceeding safe limits. Factors contributing to this situation include:
Government Initiatives and Future Planning
The Indian government has recognized the severity of air pollution and has initiated several programs to address it. Key initiatives include:
Conclusion
Addressing air pollution is a complex challenge that requires a multi-faceted approach involving governments, communities, and individuals. By raising awareness, promoting cleaner technologies, and implementing effective policies, we can work towards a healthier environment. The future of air quality depends on our collective efforts to reduce emissions, monitor pollution levels, and adopt sustainable practices. Only through collaboration and commitment can we ensure cleaner air for generations to come.



